|
Description
|
Image
|
01. Why Screening Tests Are Important
Getting the right screening test at the right time is one of the most important things a man can do for his health. Screenings find diseases early, before you have symptoms, when they're easier to treat. Early colon cancer can be nipped in the bud. Finding diabetes early may help prevent complications such as vision loss and impotence. The tests you need are based on your age and your risk factors.
|

|
02. Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer found in American men after skin cancer. It tends to be a slow-growing cancer, but there are also aggressive, fast-growing types of prostate cancer. Screening tests can find the disease early, sometimes before symptoms develop, when treatments are most effective.
|

|
03. Tests for Prostate Cancer
Screenings for healthy men may include both a digital rectal exam (DRE) and a prostate specific antigen (PSA) blood test. The American Cancer Society advises men to talk with a doctor about the risks and limitations of PSA screening as well as its possible benefits. Discussions should begin at:
* 50 for average-risk men
* 45 for men at high risk. This includes African-Americans.
* 40 for men with a strong family history of prostate cancer.
The American Urological Association recommends a first-time PSA test at age 40, with follow-ups per doctor's orders
|

|
04. Testicular Cancer
This uncommon cancer develops in a man's testicles, the reproductive glands that produce sperm. Most cases occur between ages 20 and 54. The American Cancer Society recommends that all men have a testicular exam when they see a doctor for a routine physical. Men at higher risk (a family history or an undescended testicle) should talk with a doctor about additional screening. Some doctors advise regular self-exams, gently feeling for hard lumps, smooth bumps, or changes in size or shape of the testes.
|

|
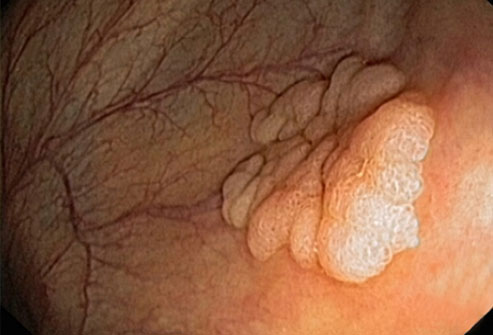
05. Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal cancer is the second most common cause of death from cancer. Men have a slightly higher risk of developing it than women. The majority of colon cancers slowly develop from colon polyps: growths on the inner surface of the colon. After cancer develops it can invade or spread to other parts of the body. The way to prevent colon cancer is to find and remove colon polyps before they turn cancerous.
|
|
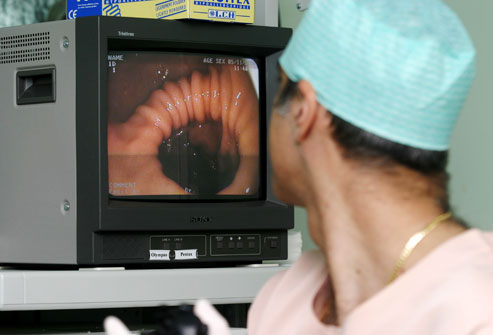
06. Tests for Colon Cancer
Screening begins at age 50 in average-risk adults. A colonoscopy is a common test for detecting polyps and colorectal cancer. A doctor views the entire colon using a flexible tube and a camera. Polyps can be removed at the time of the test. A similar alternative is a flexible sigmoidoscopy that examines only the lower part of the colon.
Some patients opt for a virtual colonoscopy — a CT scan — or double contrast barium enema — a special X-ray — although if polyps are detected, an actual colonoscopy is needed to remove them.
|
|
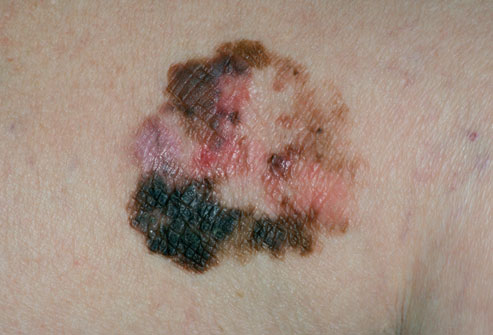
07. Skin Cancer
The most dangerous form of skin cancer is melanoma (shown here). It begins in specialized cells called melanocytes that produce skin color. Older men are twice as likely to develop melanoma as women of the same age. Men are also 2-3 times more likely to get non-melanoma basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers than women are. Your risk increases as lifetime exposure to sun and/or tanning beds accumulates; sunburns accelerate risk.
|
|
08. Screening for Skin Cancer
The American Cancer Society and the American Academy of Dermatology recommend regular skin self-exams to check for any changes in marks on your skin including shape, color, and size. A skin exam by a dermatologist or other health professional should be part of a routine cancer checkup. Treatments for skin cancer are more effective and less disfiguring when it's found early.
|

|
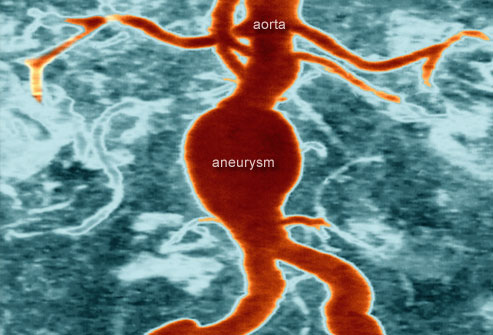
09. High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)
Your risk for high blood pressure increases with age. It's also related to your weight and lifestyle. High blood pressure can lead to severe complications without any prior symptoms, including an aneurysm — dangerous ballooning of an artery. But it can be treated. When it is, you may reduce your risk for heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure. The bottom line: Know your blood pressure. If it's high, work with your doctor to manage it.
|
|
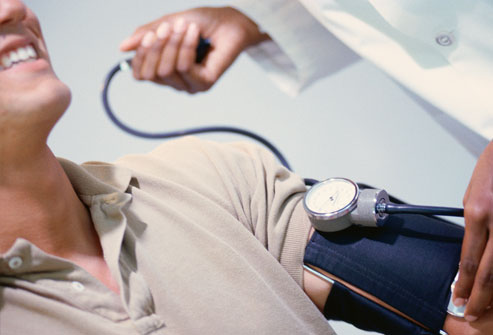
10. Screening for High Blood Pressure
Blood pressure readings give two numbers. The first (systolic) is the pressure in your arteries when the heart beats. The second (diastolic) is the pressure between beats. Normal blood pressure is less than 120/80. High blood pressure is 140/90 or higher, and in between those two is prehypertension — a major milestone on the road to high blood pressure. How often blood pressure should be checked depends on how high it is and what other risk factors you have.
|
|
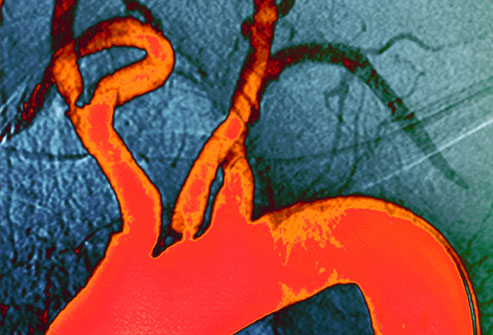
11. Cholesterol Levels
A high level of LDL cholesterol in the blood causes sticky plaque to build up in the walls of your arteries (seen here in orange). This increases your risk of heart disease. Atherosclerosis – hardening and narrowing of the arteries — can progress without symptoms for many years. Over time it can lead to heart attack and stroke. Lifestyle changes and medications can reduce this "bad" cholesterol and lower your risk of cardiovascular disease
|
|
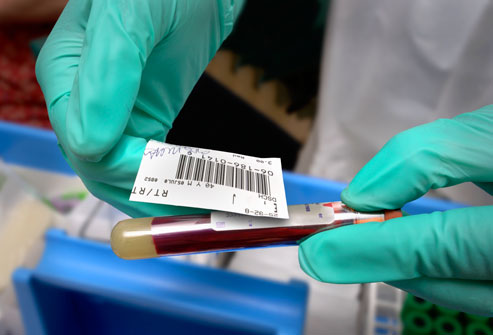
12. Determining Cholesterol Levels
The fasting blood lipid panel is a blood test that tells you your levels of total cholesterol, LDL "bad" cholesterol, HDL "good" cholesterol, and triglycerides (blood fat). The results tell you and your doctor a lot about what you need to do to reduce your risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. Men 20 years and older should have a new panel done at least every five years. Starting at 35, men need regular cholesterol testing.
|
|
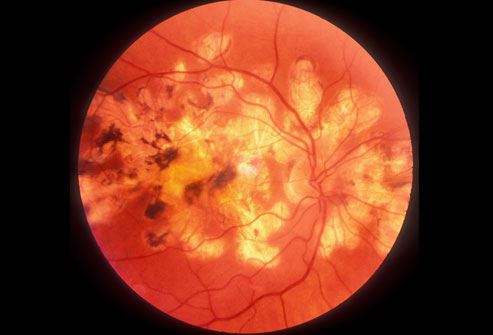
13. Type 2 Diabetes
One-third of Americans with diabetes don't know they have it. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to heart disease and stroke, kidney disease, blindness from damage to the blood vessels of the retina (shown here), nerve damage, and impotence. This doesn't have to happen. Especially when found early, diabetes can be controlled and complications can be avoided with diet, exercise, weight loss, and medications.
|
|
14. Screening for Type 2 Diabetes
A fasting plasma glucose test is most often used to screen for diabetes. More and more doctors are turning to the A1C test, which tells how well your body has controlled blood sugar over time. Healthy adults should have the test every three years starting at age 45. If you have a higher risk, including high cholesterol or blood pressure, you may start testing earlier and more frequently.
|
|
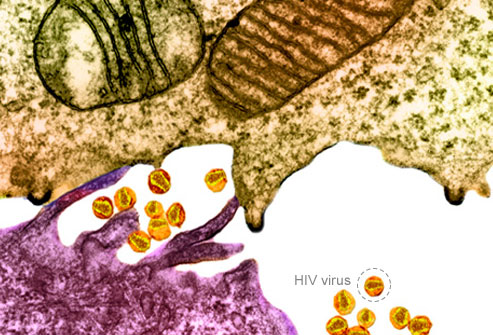
15. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
HIV is the virus that causes AIDS. It's in the blood and other body secretions of infected individuals, even when there are no symptoms. It spreads from one person to another when these secretions come in contact with the vagina, anal area, mouth, eyes, or a break in the skin. There is still no cure or vaccine. Modern treatments can keep HIV infection from becoming AIDS, but these medications can have serious side effects.
|
|
16. HIV Screening Tests
HIV-infected individuals can remain symptom-free for many years. The only way to know they are infected is with a series of blood tests. The first test is called ELISA or EIA. It looks for antibodies to HIV in the blood. It's possible not to be infected and still show positive on the test. So a second test called a Western blot assay is done for confirmation. If you were recently infected, you could still have a negative test result. Repeat testing is recommended. If you think you may have been exposed to HIV, ask your doctor about the tests.
|
|
17. Preventing the Spread of HIV
Most newly infected individuals test positive by two months after infection. But up to 5% are still negative after six months. Safe sex — abstinence or always using latex barriers such as a condom or a dental dam — is necessary to avoid getting HIV and other sexually transmitted infections. If you have HIV and are pregnant, talk with your doctor about what needs to be done to reduce the risk of HIV infection in your unborn child. Drug users should not share needles.
|

|
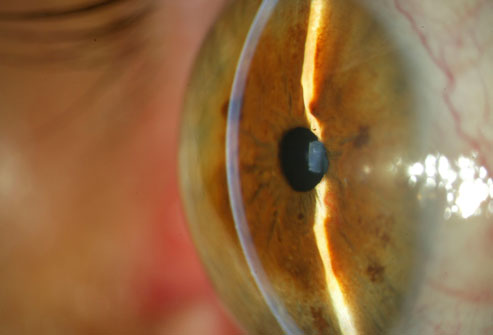
18. Glaucoma
This group of eye diseases gradually damages the optic nerve and may lead to blindness – and significant, irreversible vision loss can occur before people with glaucoma notice any symptoms. Screening tests look for abnormally high pressure within the eye, to catch and treat the condition before damage to the optic nerve.
|
|
19. Glaucoma Screening
Eye tests for glaucoma are based on age and personal risk:
* Under 40: Every 2-4 years
* 40-54: Every 1-3 years
* 55-64: Every 1-2 years
* 65 up: Every 6-12 months
Talk with a doctor about earlier, more frequent screening, if you fall in a high risk group: African-Americans, those with a family history of glaucoma, previous eye injury, or use of steroid medications.
|

|