|
Comparison
|
Plasma televisions
|
LCD televisions
|
Advantage
|
|
Screen Size
|
Screen sizes range from 32 inches to 63 inches.
Larger plasmas, like a 103 inch unit from Panasonic, are in production, but
are still prohibitively expensive for consumer use.
|
Sizes range from 13 inches to 45 inches. As with
plasma, there are larger LCD TVs made, like a 100 inch display recently
released by LG, but they are not readily available or affordable at the
consumer level.
|
Plasma TVs are the current size champions, particularly
when comparing TVs that consumers can easily purchase. LCDs
are catching up in size with their developing technology, however, and may
surpass Plasmas in the near future. This may be due to difficulties in
producing glass large enough for larger plasmas.
|
|
Viewing Angle
|
Up to 160°
|
Up to 175°
|
LCD TVs have the advantage here, but by a small
margin. Your viewing experience is not going to be ideal at 160 or 175
degree angles. LCD TVs used to have a problem in this area, primarily because
LCDs were originally used as single person
computer monitors.
|
|
Screen Refresh Rates
|
Plasma displays refresh and handle rapid movements
in video about as well as CRT televisions.
|
LCD TVs were originally designed for data display,
and not video. Therefore refresh rates had to be improved. LCD TVs with
refresh rates below 16 ms or lower (5-15 ms) show very few noticeable
artifacts. LCD TVs are now available with refresh rates as low as 5ms.
|
Slight edge to plasma technology.
|
|
Burn-in or Stuck Pixels
|
Plasma TVs can suffer from burn-in produced by
static images. After extended periods, stationary images "burn
in" and produce an after-image ghost which remains permanently on the
screen. With technologies such as 'pixel orbitor,'
new plasma TVs have addressed burn-in and significantly reduced the issues
of older models.
|
LCD TVs do not suffer from burn-in, but can have a
"retained pixel charge" which may also produce ghosting. Stuck
pixels are also possible with an LCD display.
|
With the latest plasma technology, this is less of
an issue than ever before. "Pixel orbitor,"
for example, is one method of reducing burn in used by plasma
manufacturers. It requires no additional programing
from the end user as some older burn-in prevention techniques did. If you
plan to use a plasma for gaming, some games with permanent 'dashboards' may
still cause some burn-in. Check user-manuals for
available solutions by model.
|
|
Product Life-span
|
Plasma TVs have a reported half life of 30,000 to
60,000 hours. Half-life is the time it takes the lamp to fade to half its
original brightness.
|
LCD TVs also have replaceable backlights, but the
expense of replacing one when the time comes may be greater than simply
replacing the entire TV.
|
Both Plasma and LCD technology should more than
adequately satisfy most consumers. The average CRT TV (the kind most of us
have at home) has a half-life of around 25,000 hours. If the average
American household watches an average of four to six hours of television a
day, even a 30,000 hour lamp would give you over 16 years of use. By then
you'll be enjoying your new 'Holodeck.'
|
|
Weight
|
Plasma displays are fairly heavy, and may need
additional supports to be mounted onto a wall.
|
LCD TVs weigh less than comparably sized plasma
TVs.
|
LCD TVs are considerably lighter, more portable, and
cheaper to ship.
|
|
Durability
|
Plasmas are very fragile making them tricky to
ship and install. Unlike the commercials where plasmas are mounted on the
ceiling, plasmas are best installed by a professional, and should be installed
on a wall that can bear a good deal of weight.
|
Much more durable than plasmas. End users can
easily mount an LCD TV themselves if desired.
|
LCD TVs are far less fragile than plasmas.
|
|
Shipping
|
Due to their fragile nature, plasma TVs need to be shipped by specialty carriers. Overnight or
fast delivery options are not recommended. Special shipping methods and
their heavier weight add to higher shipping costs.
|
Shipping LCD TVs is not difficult, and is not as
expensive as shipping plasma displays.
|
LCD TVs are lighter and far less fragile than
plasma displays making shipping easier and less expensive.
|
|
Installation
|
Plasmas are heavier, use more power, and run hotter
than LCD TVs, and therefore require more planning when mounting them.
Plasmas are generally best installed by professionals.
|
End users can easily install LCD TVs themselves,
or can use them just as they use a traditional TV using a stand.
|
LCD TVs are much easier to install than plasma
TVs.
|
|
Brightness/Contrast
|
Plasma TVs report higher brightness and contrast
levels than LCDs. Under ideal conditions (no
ambient light) this is a true advantage of plasma technology, because LCD
TVs are backlit and therefore light must be blocked to create blacks.
Plasmas have individual pixels that either on or off, creating deeper
blacks and better contrast.
|
LCD TVs can often look better in 'real-world' situations.
Plasmas are made with a special glass surface that can reflect light, which
dulls the brightness and contrast of the image. LCD TVs reflect very little
light, allowing them to maintain levels in well-lit rooms.
|
Both LCD and plasma TVs will meet the brightness
expectations of most consumers. However, in 'real world' situations with
ambient light, LCD TVs will generally look a little brighter.
|
|
Thickness
|
As thin as 3 inches deep.
|
As thin as 2 inches deep.
|
LCDs TVs are just a bit thinner.
|
|
Performance at High Altitude
|
High altitudes can affect the performance of
plasma displays because the gas held inside each pixel is stressed, and has
to work harder to perform. Some manufacturers make plasmas that are
specifically designed for high-altitudes, but they may be priced higher
than standard models.
|
LCD TVs are not affected by high altitudes.
|
LCD TVs.
|
How Plasma Works
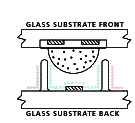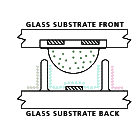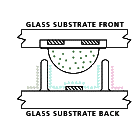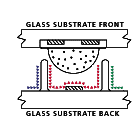 Plasma is a
flat, lightweight surface covered with millions of tiny glass bubbles. Each
bubble contains a gas-like substance, the plasma, and has a phosphor coating.
Think of the bubbles as the pixels. Plasma is a
flat, lightweight surface covered with millions of tiny glass bubbles. Each
bubble contains a gas-like substance, the plasma, and has a phosphor coating.
Think of the bubbles as the pixels.
Now, think of each pixel-bubble as having three sub-pixels
- one red, one green, one blue. When it is time to display an image signal (RGB
or video), a digitally controlled electric current flows through the flat
screen, causing the plasma inside designated bubbles to give off ultraviolet
rays. This light in turn causes the phosphor coatings to glow the appropriate
color.
Millions of RGB bubbles glow and dim to make a rich, vivid
image on your plasma TV.
How LCD TVs Work
What Is LCD Technology?
 Like popular
LCD monitors you commonly see used with computers, LCD TVs have a slim design
and a flat viewing surface, but have been fine tuned for video display. Recent
advances in flat panel LCD technology now allow for larger screens, wider
viewing angles, and higher-quality video images. LCD TVs are also competition
for trendy-but-heavy, plasma display technology. They are several times lighter
than comparably sized plasmas, and are far more durable. Like popular
LCD monitors you commonly see used with computers, LCD TVs have a slim design
and a flat viewing surface, but have been fine tuned for video display. Recent
advances in flat panel LCD technology now allow for larger screens, wider
viewing angles, and higher-quality video images. LCD TVs are also competition
for trendy-but-heavy, plasma display technology. They are several times lighter
than comparably sized plasmas, and are far more durable.
How do LCD TV's work?
Two sheets of polarized transparent material, one with a
special polymer coating that holds liquid crystals, are adhered together.
Electric current is passed through individual crystals, which interpret the
information from the broadcast signal to allow or disallow light through them
to create an image. The crystals themselves do not produce light, so the
technology is "non-emissive" and therefore does not give off
radiation like an older television does. Fluorescent tubes housed behind the
transparent material illuminate the image. They require less power to operate
than CRT and plasma televisions which require powering hundreds of electrodes
to stimulate the phosphorous.
LCD TVs At-A-Glance:
- Use
non-emissive technology; do not emit radiation.
- Use
fluorescent tubes which require less power to operate.
|